Definition and responsibilities
A production worker is a key member of the manufacturing process, responsible for assembling products, operating machinery, and ensuring that production targets are met. Their duties can vary widely depending on the industry and specific job requirements but generally include:
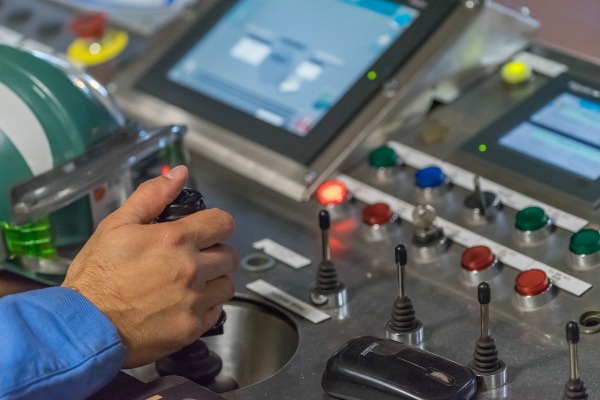
Operating machinery - Production workers are often tasked with running and maintaining equipment used in the manufacturing process. This includes setting up machines, monitoring their operation, and performing routine maintenance to prevent breakdowns.
Assembling products - Whether it’s electronics, automobiles, or consumer goods, production workers assemble components to create finished products. This requires precision and attention to detail to ensure quality standards are met.
Quality control - Ensuring that products meet specified standards is a critical responsibility. Production workers inspect materials and finished goods, identify defects, and implement corrective actions to maintain quality.
Packaging and labeling - Once products are assembled and inspected, production workers may be involved in packaging and labeling, preparing items for distribution and sale.
Inventory management - Keeping track of materials and supplies is essential to avoid production delays. Production workers monitor inventory levels, reorder supplies when necessary, and manage storage areas efficiently.
Essential skills and qualifications
The role of a production worker demands a diverse set of skills and qualifications to handle the complexities of modern manufacturing environments effectively. Key competencies include:
Technical proficiency - Understanding how to operate and troubleshoot machinery is fundamental. Production workers must be comfortable with various types of equipment and often require specific training or certifications.
Attention to detail - Precision is crucial in manufacturing to ensure products meet quality standards. Production workers must be meticulous in their tasks, identifying and addressing any discrepancies.
Physical stamina - The job often involves standing for long periods, lifting heavy objects, and performing repetitive tasks. Physical endurance and strength are necessary to handle these demands.
Problem-solving abilities - Production workers frequently encounter issues such as equipment malfunctions or material shortages. The ability to quickly identify problems and implement effective solutions is invaluable.
Communication skills - Effective communication with team members and supervisors ensures smooth operations. Production workers must convey information clearly and collaborate efficiently to achieve common goals.
Adaptability - The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving with new technologies and processes. Production workers must be adaptable, willing to learn new skills, and embrace changes to stay relevant.
Impact of technology on production workers
Advancements in technology have significantly reshaped the role of the production worker, introducing both challenges and opportunities. Key technological impacts include:
Automation and robotics - The integration of automated systems and robots has transformed many manufacturing processes. While this has increased efficiency and reduced the need for manual labor in certain areas, it has also necessitated that production workers develop new technical skills to operate and maintain these advanced systems.
Industry 4.0 - The fourth industrial revolution emphasizes interconnectedness and data-driven decision-making. Production workers now interact with smart machines and use real-time data to optimize production processes, enhancing productivity and quality.
Digital tools and software - Modern manufacturing relies on various digital tools for tasks such as inventory management, quality control, and production planning. Proficiency in these software applications is increasingly important for production workers to perform their duties effectively.
Remote monitoring and control - Technology enables remote monitoring of production lines, allowing workers to oversee operations from different locations. This flexibility can improve efficiency but also requires workers to be adept at using remote control systems and troubleshooting issues from afar.
Training and development opportunities
To thrive in the evolving manufacturing landscape, production workers must engage in continuous training and professional development. Key areas of focus include:
Technical training: - As machinery and technology advance, ongoing training is essential to keep production workers up-to-date with the latest equipment and processes. This may involve on-the-job training, workshops, or formal education programs.
Skill enhancement - Developing additional skills, such as programming for automated systems or advanced quality control techniques, can enhance a production worker’s capabilities and career prospects.
Safety training - Ensuring workplace safety is paramount. Production workers must receive regular training on safety protocols, emergency procedures, and the proper use of protective equipment to minimize risks and maintain a safe working environment.
Leadership development - For those aspiring to move into supervisory or management roles, leadership training can provide the necessary skills in team management, conflict resolution, and strategic planning.
Challenges faced by production workers
Despite the advancements and opportunities, production workers encounter several challenges in their roles:
Workplace safety - Manufacturing environments can be hazardous, with risks of accidents, exposure to harmful substances, and ergonomic issues. Maintaining safety standards and preventing workplace injuries remain ongoing challenges.
Job security - The rise of automation and outsourcing can threaten job security for production workers. Staying relevant through continuous learning and adapting to new technologies is crucial to mitigate this risk.
Workplace stress - High production targets, tight deadlines, and the pressure to maintain quality can lead to significant stress for production workers. Managing stress and maintaining mental health are important aspects of sustaining a productive workforce.
Skill gaps - As the industry evolves, there may be gaps between the skills production workers possess and those required by new technologies. Addressing these gaps through training and education is essential for workforce sustainability.
Future trends shaping production work
The future of production work is poised to be shaped by several emerging trends that promise to further transform the manufacturing landscape:
Increased automation - Automation will continue to expand, taking over more repetitive and hazardous tasks. This shift will allow production workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities, enhancing overall productivity.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning - AI and machine learning technologies will play a larger role in optimizing production processes, predictive maintenance, and quality control. Production workers will need to collaborate with these intelligent systems, leveraging their capabilities to improve manufacturing outcomes.
Sustainable manufacturing - There is a growing emphasis on sustainability in manufacturing. Production workers will increasingly engage in practices that reduce waste, conserve energy, and promote environmentally friendly production methods.
Customization and flexibility - As consumer demand shifts towards personalized products, manufacturing processes must become more flexible. Production workers will need to adapt to varied production requirements and rapidly changing product specifications.
Globalization and supply chain integration - Global supply chains require production workers to understand and manage complex logistics, ensuring seamless integration and timely delivery of materials and products.
The role of the production worker is integral to the success of modern manufacturing operations. As the industry continues to evolve with technological advancements and shifting market demands, production workers must adapt by acquiring new skills, embracing change, and maintaining a commitment to quality and safety. By understanding the complexities and opportunities within their roles, production workers can contribute significantly to the efficiency, innovation, and sustainability of the manufacturing sector. Investing in training and development, addressing workplace challenges, and staying attuned to future trends will ensure that production workers remain a vital and dynamic component of the industrial workforce.